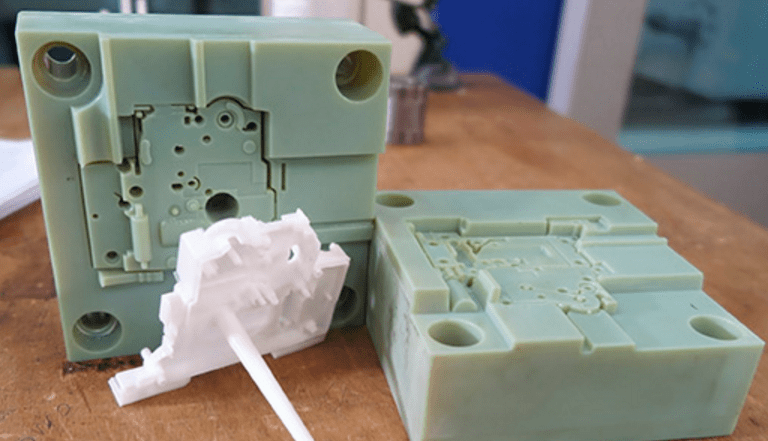
The use of 3D printing for manufacturing injection moulds allows for prototypes to be made quickly and with high precision. The purpose of this system is accelerating and perfecting the design of the final part before mass production. In this article we analyse the advantages and disadvantages of this revolutionary system which is gradually being adopted by mechanical component manufacturing companies. Let’s begin.
You will find this article interesting: Multi-material injection moulding: main techniques and advantages
What are the advantages of the manufacturing of injection moulds using 3D printers?
- The use of 3D printers for the development of injection moulds allows for the acceleration of part prototyping. Thus, injection moulds can be manufactured in just a few hours, while conventional methods take days or weeks.
- Customisation in the creation of injection moulds can be as immediate and frequent as the team of engineers deems necessary, which makes these types of machines the perfect ally during product development processes, with the purpose of attaining more certainty and a lower probability of error during the production phase.
- A shorter, more flexible process translates into a notable reduction in costs and times, with shorter delivery periods.
- Some injection moulds created with ABS material may yield moulds with a microscopic precision and layer resolution (30 microns), with a precision in excess of 0.1 mm. This advantage allows for a highly detailed prototyping that is faithful to the final part.
- It is not necessary to do any pre-programming when creating PolyJet moulds. Once the files with the design are loaded in CAD, 3D printers start printing the part without the need for manually handling the machine.
- There is a possibility to incorporate different materials in the injection moulds that are also more affordable than those used in conventional moulds: thermoset, PoliJet, thermoplastics, acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), etc.
- These machines are capable of quickly printing complex geometrical shapes.
- Lastly, this technique minimises the risk of errors in the machining of a metallic mould, if a test unit has previously been manufactured via 3D printing. Therefore, we can make one or several tests in the injection moulding machine to prepare an initial set of parts. With these parts, the manufacturer can objectively verify whether the design of the mould is adequate or if, on the contrary, it is necessary to perform some modification before machining.
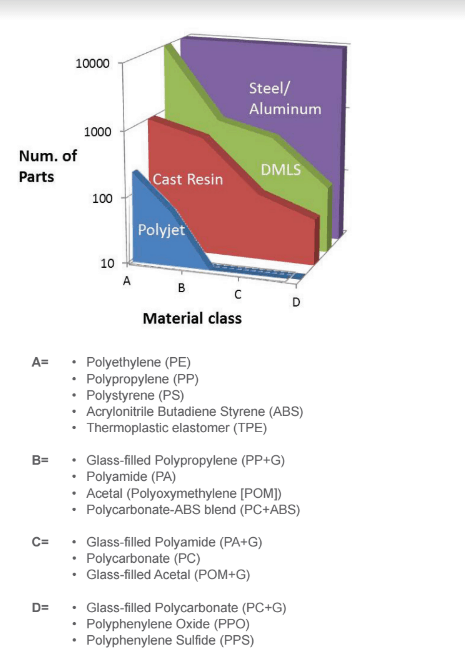
Part projection depending on the type of 3D printing material. Source: Stratasys
You may like this article: Actuators in injection systems: improving fuel efficiency and emissions
What are the limits for the 3D printing of injection moulds?
- There are still size limitations when making small-sized moulds with certain materials.
- Compaction and quality of the materials is inferior to that of injected moulds.
- Material durability confines the use of these moulds to part prototyping. These materials are not suitable for mass production; they can only be used for small productions and prototyping. To address this, high-performance plastics such as tribo-filament are being rolled out, whose resistance to wear is starting to offer results that are comparable to those of conventional injection moulding in some cases.
Some applications of injection moulds with 3D technology
Automotive and aeronautics are the sectors that are working the most with 3D printed moulds to design their prototyping parts. Creation of these moulds using conventional injection moulding machines results in higher costs and time delays in the face of any revision of the developed design. These injection moulds are ideal for highly complex sectors that are required to constantly innovate with the purpose of ensuring their leadership on the market.
Recommended reading: Plastic Injection Moulding: new technologies and applications
CLR, expert in injection technologies for the manufacturing of mechanical parts
CLR, Compañía Levantina de Reductores, has the technology, experience and know-how to manufacture moulds and develop parts with injection mould technologies. As a manufacturer of mechanical components, CLR is skilled in the mechanisation and production of parts through microinjection and overinjection or multi-component injection moulding.
Are you looking for an engineering partner for manufacturing small mechanical parts? CLR designs and manufactures speed reducers and all sorts of mechanical components to build gear boxes: gears, pinions, washers, plain bearings, worm wheels… Contact our engineering team and we will help you design the parts you need with the utmost professionalism and quality.