Due to its sophistication, agility and precision, the automotive industry is considered to be an “industry of knowledge”. There is a true halo of innovation surrounding it, being one of the most dynamic industries, especially in regards to vehicle electromechanics.
We often see how major OEM manufacturers introduce new technologies where safety and comfort at the wheel are in the spotlight. In this article we will discuss a few trends and projects that are taking over the most important mechanical innovations of the sector.
Automatic electronic clutches
The first electronic clutch was designed and developed for the first time by Fadiel Italiana, and became famous due to its similarity to a duck’s head – it is now known as duck clutch.
These clutches were first applied to vehicles specially adapted for handicapped drivers, since the gear stick-operated clutch allowed for the substitution of the foot clutch.
It has now been Bosch Automotive, the German manufacturer of automotive components, who has developed the eClutch automatic electronic clutch which reduces fuel consumption by 5%.
One of the main advantages when compared to other clutches is that it incorporates an automation that shifts to neutral when the driver is not accelerating the vehicle.
Adaptive headlights
One of the items of vehicle safety which has become widespread is adaptive headlights.
Night driving is always a delicate issue, and enhancing visibility and safety in adverse lighting conditions is a true obsession for many R&D managers of OEM manufacturers. Here, we could make a special mention of Ford’s dynamic LED technology, a brand that is always at the forefront of safety systems. Specifically, this system is capable of adjusting the lighting pattern of the headlights depending on the speed, the environment and a myriad of conditions.
The system covers up to eight different types of situations to address scenarios both in the city, and when facing adverse atmospheric conditions.
Driver assistance systems
Based on smart sensor technology, driver assistance systems constantly analyse the driver’s behaviour to detect critical situations. Those sensors activate different automations that dynamically and electromechanically operate the steering wheel and front pedals with the purpose of mitigating the consequences of an accident.
Audi offers assistance systems that not only revolutionise the driver’s experience, but are also a clear sign of the future of mobility. An example of this is the traffic jam assist, available in the Audi A4 and Audi Q7 models. When the driver is in a traffic jam, the system uses a radar, ultrasonic sensors and a camera to identify vehicles located in front and in adjacent lanes. From that moment, the vehicle’s steering is automated as long as the speed does not exceed 65km/h.
This is how the parking assistant works
The race of vehicle electromechanics to improve sustainability
In the context of an increasingly environmentally-aware planet, the automotive sector strives to improve vehicles in order to reduce noxious gas emissions. These breakthroughs influence the budget and the eco-awareness of the buyers, becoming a competitive and powerful selling point.
With this in mind, FEV engineers, a world leader in the development of vehicle engines, have found a way to create greater engine compression in order for the vehicle to use less fuel. Specifically, they have redesigned the traditional conrod that connects the piston to the crankshaft, thereby optimising the engine’s efficiency and allowing it to deploy its full power. This innovation ensures 7% fuel savings. Engines such as Ford’s Ecoboost or BMW’s TwinPower are clear examples of the application of this technology, which improve and optimise combustion and injection.
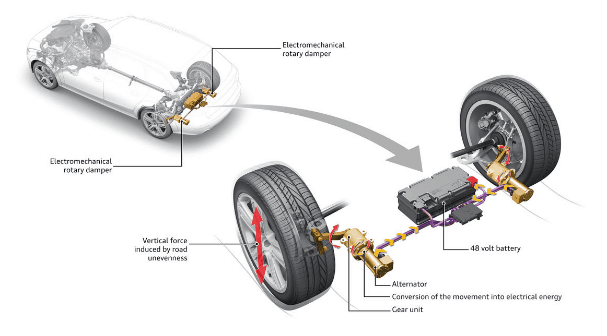
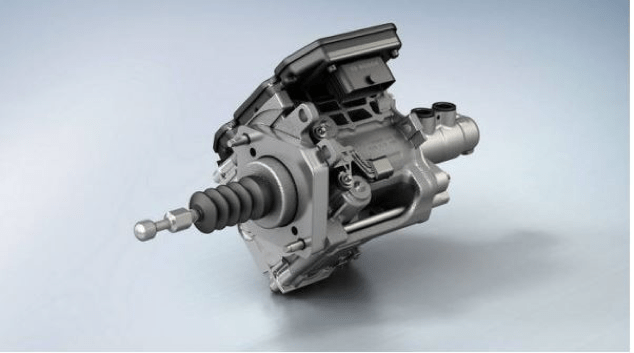
New electromagnetic suspension systems
Since the mythical Citroën DS and its hydropneumatic suspension, the automotive industry has introduced a myriad of technological proposals to improve vehicle suspensions.
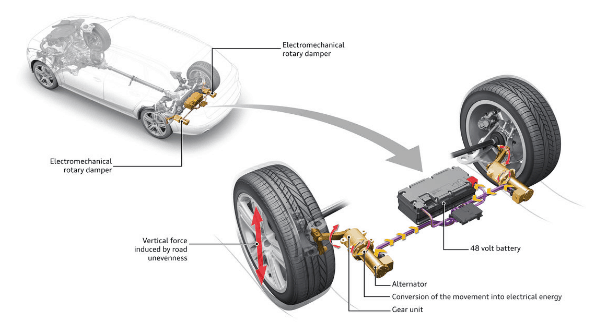
During the last few years, adaptive suspension systems have become the norm among many manufacturers. When facing this trend, Audi has once again proven its position of leadership in innovation and has recently introduced the eRoot system. As we already explained in our post, ‘The best electromechanical engineering projects’, this system stands out since it uses electromechanical rotary shock absorbers instead of the traditional telescopic hydraulic ones.
The main novelty of these dampers is that they reuse the energy generated on every dip to turn it into electricity.
Were you aware of these innovations? As you have seen, we have spoken about many applications of vehicle electromechanics, and behind each of them, there were clear protagonists: electric actuators. Even when they are not the most important components, the precision attained by these parts has considerably influenced the emergence of new motions in the most adverse environments.
CLR, a company with a long track record in the design and manufacturing of actuation mechanisms is used to providing motion solutions in Tier 1 projects. As a result of its experience in these businesses, this company from Alicante has just released a free guide to improve the management of suppliers in automation. Are you interested? Do not hesitate to download it by clicking in this picture.